Posthaste: Deeper Canadian Recession Predicted Despite Tariff Reductions
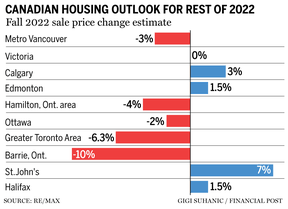
Table of Contents
Weakening Global Economy Impacts Canada
The ripple effects of a slowing global economy are significantly impacting Canada's economic health. The interconnected nature of the global market means that slowdowns in other countries directly translate into challenges for Canadian businesses and consumers. This global recession is exacerbating existing vulnerabilities in the Canadian economy.
- Reduced demand for Canadian exports: Declining global demand, particularly for Canadian commodities like oil and lumber, is hitting export-reliant sectors hard. This export decline is contributing directly to a slower overall growth rate.
- Decreased foreign investment: Uncertainty in the global market is making foreign investors hesitant to commit capital to Canada, further hindering economic expansion. The slowdown in foreign investment slowdown is impacting job creation and investment in new projects.
- Impact of global inflation on Canadian consumers and businesses: High inflation globally is driving up the cost of imported goods, increasing inflation within Canada and squeezing household budgets and corporate profits. This cost of living crisis is squeezing household budgets, leading to decreased consumer spending.
- The ongoing economic struggles in key trading partners like the United States and Europe are directly impacting Canada’s economic performance. Their reduced purchasing power translates into less demand for Canadian goods and services.
- Keywords: global recession, export decline, foreign investment slowdown, global inflation, cost of living crisis.
High Interest Rates Stifle Growth
The Bank of Canada's aggressive interest rate hikes, aimed at combating inflation, are inadvertently stifling economic growth. While necessary to control inflation, these increases are having a chilling effect on borrowing and investment.
- Increased borrowing costs for businesses and consumers: Higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive for businesses, reducing their ability to invest in expansion and hiring. Consumers face increased costs for mortgages, loans, and credit card debt, leading to reduced spending.
- Reduced consumer spending and business investment: Higher borrowing costs directly translate to less consumer spending and reduced business investment, creating a negative feedback loop that slows economic activity. This reduced consumer spending is further dampening economic growth.
- Impact on the housing market: The Canadian housing market, a significant driver of the economy, is particularly vulnerable to interest rate hikes. Higher mortgage rates are cooling the market, leading to price corrections and impacting related industries.
- Keywords: interest rate hikes, monetary policy, housing market downturn, borrowing costs.
Inflation Remains Stubbornly High
Despite interest rate increases, inflation remains stubbornly high, eroding purchasing power and increasing production costs for businesses. This persistent inflation is a major factor contributing to the deeper Canadian recession prediction.
- Erosion of purchasing power: High inflation reduces the real value of wages and savings, forcing consumers to cut back on spending, further slowing economic growth. This erosion of purchasing power is forcing consumers to make difficult choices.
- Increased production costs for businesses: Rising input costs, from raw materials to energy, are squeezing profit margins for businesses, potentially leading to layoffs and reduced investment. These increased production costs are impacting profitability across various sectors.
- Wage stagnation lagging behind inflation: Wage growth has not kept pace with inflation, leaving many Canadians with reduced real income and further dampening consumer spending. The wage stagnation is contributing to the overall economic slowdown.
- Keywords: inflation, cost of living, wage growth, purchasing power.
Limited Effectiveness of Tariff Reductions
While tariff reductions are typically intended to stimulate economic activity, their impact has been limited in this case. The global economic headwinds are proving stronger than the benefits derived from these cuts.
- Global economic headwinds outweigh the benefits of tariff cuts: The current global economic slowdown is so significant that the positive effects of tariff reductions are being overshadowed by broader economic weakness. These global economic headwinds are significantly impacting the Canadian economy.
- Export-oriented sectors, particularly those reliant on global demand, are still struggling despite the tariff cuts. The global slowdown continues to pose a significant challenge.
- Internal economic factors, such as high debt levels and the cooling housing market, are also dampening the positive effects of the tariff reductions. These internal economic factors are further contributing to the economic slowdown.
Potential Implications of a Deeper Recession
A prolonged and deeper Canadian recession carries significant risks across various sectors of the economy and society as a whole.
- Increased unemployment: A deeper recession will likely lead to a significant increase in unemployment, putting further strain on households and increasing social support demands. The rising unemployment rate is a key concern.
- Government debt increase: Increased government spending on social programs and reduced tax revenue will likely lead to a further increase in government debt. The rising fiscal deficit is a major challenge.
- Social unrest and political instability: Economic hardship can often lead to social unrest and political instability, posing significant challenges for the government. The social impact of a deeper recession is concerning.
- Keywords: unemployment rate, fiscal deficit, social impact, social unrest, political instability.
Conclusion: Navigating the Deeper Canadian Recession
The predicted deeper Canadian recession is driven by a confluence of factors: a weakening global economy, high interest rates, persistent inflation, and the limited effectiveness of recent tariff reductions. The severity of the predicted deeper Canadian recession necessitates proactive measures. While the outlook remains uncertain, a cautious approach is warranted. Stay informed about the evolving deeper Canadian recession and its impact on your finances. Consult financial advisors and develop strategies to weather this economic storm. Understanding the nuances of this deeper Canadian recession is crucial for navigating the challenges ahead.

Featured Posts
-
 Toute L Actualite Boursiere Du Lundi 24 Fevrier Sur Bfm Bourse
Apr 23, 2025
Toute L Actualite Boursiere Du Lundi 24 Fevrier Sur Bfm Bourse
Apr 23, 2025 -
 11th Inning Walk Off Bunt Sinks Royals Against Brewers
Apr 23, 2025
11th Inning Walk Off Bunt Sinks Royals Against Brewers
Apr 23, 2025 -
 V Mware Costs To Skyrocket 1050 At And Ts Concerns Over Broadcoms Acquisition
Apr 23, 2025
V Mware Costs To Skyrocket 1050 At And Ts Concerns Over Broadcoms Acquisition
Apr 23, 2025 -
 Pavel Pivovarov Predstavil Merch S Aleksandrom Ovechkinym
Apr 23, 2025
Pavel Pivovarov Predstavil Merch S Aleksandrom Ovechkinym
Apr 23, 2025 -
 M3 As Autopalya Forgalomkorlatozasok Utlezarasok Es Elorejelzesek
Apr 23, 2025
M3 As Autopalya Forgalomkorlatozasok Utlezarasok Es Elorejelzesek
Apr 23, 2025
