Toxic Chemicals From Ohio Train Derailment: A Building Contamination Investigation
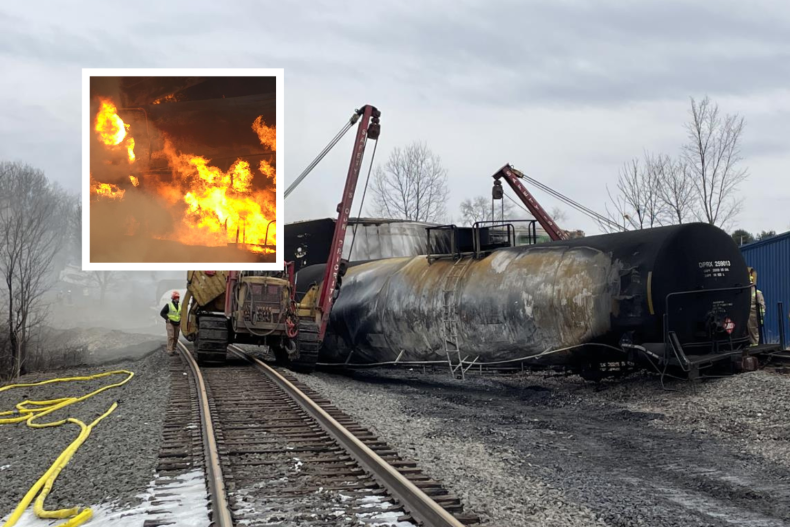

Table of Contents
Identifying the Toxic Chemicals Involved
The Ohio train derailment resulted in the release of several hazardous chemicals, posing significant risks to both human health and the environment. Key chemicals included vinyl chloride, butyl acrylate, and ethylene glycol monobutyl ether. These substances present various health hazards depending on exposure levels and duration.
-
Vinyl Chloride: This colorless gas is a known human carcinogen, linked to liver cancer and other serious health problems. Long-term exposure can lead to liver damage and a rare form of blood vessel cancer called angiosarcoma.
-
Butyl Acrylate: Exposure to butyl acrylate can cause respiratory irritation, skin sensitization, and eye irritation. Inhalation can lead to coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
-
Ethylene Glycol Monobutyl Ether: This chemical is known to cause irritation to the eyes, skin, and respiratory tract. It can also affect the central nervous system.
The unique properties of these chemicals influence their persistence and potential impact on building materials. For example, vinyl chloride's volatility means it can easily permeate building materials, while others may adsorb onto surfaces, leading to long-term contamination. The long-term health consequences of exposure to these chemicals, even at low levels, remain a significant concern requiring ongoing monitoring and research.
Assessing the Extent of Environmental Contamination
The geographical area affected by the chemical spill extends beyond the immediate vicinity of the derailment site. Initial assessments focused on the immediate area, but the potential for broader contamination necessitates a comprehensive environmental investigation.
The extent of contamination is being evaluated through various methods, including:
- Air Quality Testing: Monitoring air samples for the presence of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), including those released in the derailment.
- Soil Sampling and Analysis: Collecting soil samples to determine the level of chemical infiltration and the extent of soil contamination.
- Water Testing: Analyzing water sources for the presence of dissolved chemicals, assessing potential groundwater contamination.
Mapping the affected areas is crucial for guiding remediation efforts. Challenges in accurately assessing the extent of contamination include:
- Inaccessible areas: Difficult-to-reach areas may remain untested, potentially harboring hidden contamination.
- Long-term effects: The long-term impact of the chemicals on the environment and its persistence in soil and groundwater requires ongoing monitoring.
Investigating Building Contamination
Investigating building contamination requires a systematic approach using specialized techniques. Procedures include:
- Air Quality Testing: Analyzing indoor air for the presence of VOCs using sensitive instruments.
- Surface Sampling: Collecting samples from various surfaces (walls, floors, furniture) to identify chemical residues.
- Material Analysis: Testing building materials (e.g., drywall, insulation) to determine the extent of chemical absorption.
Identifying contaminated areas involves a detailed assessment of the building's structure and systems. A comprehensive building contamination investigation involves:
- Sample Collection: Carefully collecting representative samples using appropriate techniques to avoid cross-contamination.
- Laboratory Analysis: Sending samples to accredited laboratories for analysis to identify and quantify the specific chemicals present.
- Report Generation: Preparing a detailed report summarizing the findings, identifying contaminated areas, and recommending remediation strategies.
Remediation and Mitigation Strategies
Remediation strategies for contaminated buildings vary depending on the extent and type of contamination. Options include:
- Air Purification: Using specialized air filtration systems to remove airborne contaminants.
- Decontamination: Cleaning and treating surfaces to remove chemical residues.
- Material Removal: Removing and disposing of severely contaminated building materials.
The cost implications of remediation can be substantial, depending on the size of the building, the extent of contamination, and the chosen remediation methods. Protecting building occupants during remediation is paramount, involving protective measures such as evacuation, respiratory protection, and the use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE). Preventative measures to minimize future contamination risks include:
- Improved chemical transportation safety regulations.
- Enhanced emergency response planning.
- Regular environmental monitoring near industrial sites.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
The Ohio train derailment highlights the importance of understanding environmental regulations and liabilities. Relevant legislation, such as the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA), governs the cleanup of hazardous waste sites.
Building owners and residents have legal recourse to seek compensation for damages caused by the contamination. Government agencies, including the EPA and state environmental agencies, play crucial roles in overseeing the investigation, remediation, and enforcement of environmental regulations.
Building owners and residents have rights and responsibilities, including:
- The right to a safe and healthy living environment.
- The responsibility to cooperate with investigations and remediation efforts.
Conclusion: Understanding and Addressing Building Contamination from the Ohio Train Derailment
The Ohio train derailment underscores the potential for widespread building contamination following the release of toxic chemicals. Thorough investigation and appropriate remediation are crucial to mitigate health risks and restore affected properties. The long-term health implications of exposure to these chemicals highlight the need for continuous monitoring and proactive measures.
If you suspect building contamination from the Ohio train derailment, seek professional help immediately. Contact relevant authorities and environmental specialists to conduct a thorough building contamination investigation and implement necessary remediation strategies. Learn more about toxic chemicals and their impact on health and the environment to protect yourself and your community.

Featured Posts
-
 Middle Managers The Unsung Heroes Of A Thriving Workplace And Productive Teams
Apr 22, 2025
Middle Managers The Unsung Heroes Of A Thriving Workplace And Productive Teams
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Hegseth Family Involved In Military Plan Discussion Via Signal App
Apr 22, 2025
Hegseth Family Involved In Military Plan Discussion Via Signal App
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Anchor Brewing Companys Legacy Reflecting On 127 Years Of Brewing
Apr 22, 2025
Anchor Brewing Companys Legacy Reflecting On 127 Years Of Brewing
Apr 22, 2025 -
 T Mobile To Pay 16 Million For Data Breaches Spanning Three Years
Apr 22, 2025
T Mobile To Pay 16 Million For Data Breaches Spanning Three Years
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Cassidy Hutchinsons January 6th Memoir What To Expect This Fall
Apr 22, 2025
Cassidy Hutchinsons January 6th Memoir What To Expect This Fall
Apr 22, 2025
