Tariffs And China: The Impact On Export-Driven Economy
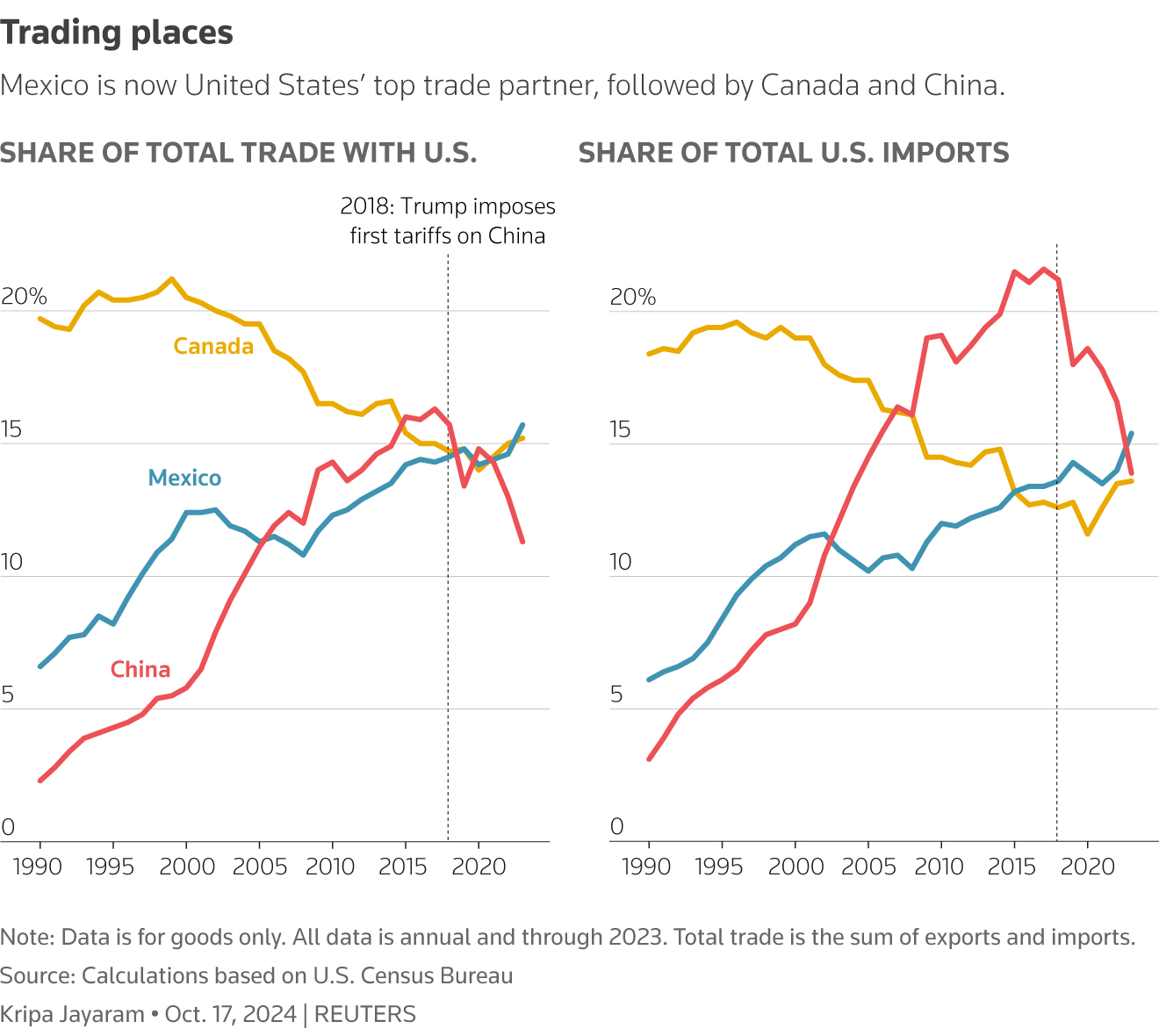
Table of Contents
The Direct Impact of Tariffs on Chinese Exports
The imposition of tariffs has had a direct and demonstrable impact on Chinese exports, leading to a multifaceted crisis for many industries.
Reduced Export Volume and Revenue
Tariffs, acting as a tax on imported goods, have directly reduced the volume and value of Chinese exports to key markets, particularly the US and EU. This decline has been especially pronounced in sectors highly reliant on these markets.
- Examples of severely impacted industries: Textiles, electronics, agricultural products (soybeans, for example), and steel have experienced significant export declines.
- Quantifiable data showing the decrease: Reports from organizations like the WTO and the Chinese customs administration reveal substantial percentage drops in export value and volume since the implementation of tariffs. Specific figures should be inserted here based on the most up-to-date data available. For instance, one could mention a specific percentage drop in textile exports to the US during a particular period.
- Impact on specific provinces: Coastal provinces like Guangdong and Zhejiang, heavily reliant on export-oriented manufacturing, have experienced disproportionately higher economic slowdowns compared to inland provinces.
Increased Production Costs and Reduced Competitiveness
Tariffs haven't just impacted export volumes; they've also increased production costs, eroding the competitiveness of Chinese businesses in the global market.
- Supply chain disruptions: Tariffs on intermediate goods and raw materials have disrupted established supply chains, increasing costs and lead times.
- Impact on profit margins and business viability: Many businesses, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), have seen their profit margins squeezed or have become entirely unviable due to increased costs. This has led to business closures and job losses.
- Comparison of Chinese export prices: Analyzing Chinese export prices before and after the implementation of tariffs demonstrates a clear increase in prices, making Chinese goods less attractive compared to competitors.
Indirect Effects on China's Domestic Economy
The impact of tariffs extends beyond the direct effect on exports, creating ripple effects across China's domestic economy.
Job Losses and Unemployment
The decline in exports has inevitably led to significant job losses across various sectors in China.
- Statistics on job losses: Data on job losses in export-oriented industries needs to be included here, referencing reliable sources such as government reports or independent research.
- Impact on wages and worker displacement: Job losses have resulted in decreased wages and increased competition for remaining jobs, impacting the livelihoods of millions of Chinese workers.
- Government initiatives: The Chinese government has implemented various initiatives to mitigate unemployment, including job training programs and stimulus packages, but the effectiveness of these measures is still under debate.
Impact on Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
Tariffs have also negatively affected foreign direct investment (FDI) in China.
- Investor sentiment and reduced confidence: Uncertainty surrounding trade policies has dampened investor sentiment and reduced confidence in the long-term stability of the Chinese market.
- Impact on specific sectors: Sectors heavily reliant on exports, such as manufacturing and technology, have seen a decrease in FDI inflows.
- Comparison of FDI inflow: A comparison of FDI inflow before and after the tariff increases is crucial to demonstrate the negative impact on investment.
Shifting Global Trade Dynamics
The imposition of tariffs has forced China to adapt by exploring new export markets and diversifying its economy.
- Strengthening ties with other countries: Initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative demonstrate China's efforts to strengthen economic ties with countries outside of the US and EU.
- Success of diversifying export markets: Assessing the success of this diversification requires analyzing the growth of exports to new markets and the overall contribution to economic growth.
- Development of domestic consumption: China is also actively promoting domestic consumption to reduce its reliance on exports, but this transition is a long-term process.
Conclusion
The imposition of tariffs has had a significant and multifaceted impact on China's export-driven economy. The direct consequences include reduced export volume and revenue, increased production costs, and reduced competitiveness. Indirectly, tariffs have led to job losses, decreased foreign investment, and forced China to re-evaluate its global trade strategy. While China has taken steps to diversify its markets and promote domestic consumption, the long-term effects of these tariffs remain to be seen. Understanding the intricate relationship between tariffs and China's economy is crucial for businesses and policymakers alike. Further research into the long-term effects of tariffs and China's economy is essential for navigating this evolving global trade landscape. Staying informed about the latest developments regarding tariffs and China's export-driven economy is vital for making strategic decisions in this dynamic environment.

Featured Posts
-
 Fsu Security Breach Swift Police Response Fails To Quell Student Fears
Apr 22, 2025
Fsu Security Breach Swift Police Response Fails To Quell Student Fears
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Blockchain Analytics Leader Chainalysis Integrates Ai Through Alterya Purchase
Apr 22, 2025
Blockchain Analytics Leader Chainalysis Integrates Ai Through Alterya Purchase
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Office365 Hacker Made Millions Targeting Executives
Apr 22, 2025
Office365 Hacker Made Millions Targeting Executives
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Lab Owner Admits To Falsifying Covid 19 Test Results
Apr 22, 2025
Lab Owner Admits To Falsifying Covid 19 Test Results
Apr 22, 2025 -
 The Fracturing Relationship Understanding The Breakdown In U S China Relations And Its Implications
Apr 22, 2025
The Fracturing Relationship Understanding The Breakdown In U S China Relations And Its Implications
Apr 22, 2025
