Few Places To Hide: Posthaste Analysis Of Trump's Tariffs And Canadian Households
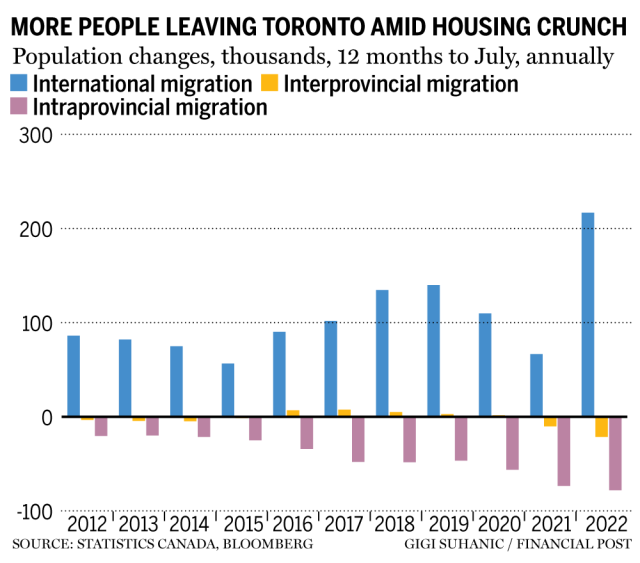
Table of Contents
H2: The Immediate Impact on Canadian Consumer Prices
The immediate impact of Trump's tariffs was a sharp increase in the cost of everyday goods for Canadian consumers. This "tariff impact" manifested in several key ways:
H3: Increased Costs of Everyday Goods
Tariffs on steel, aluminum, and lumber, key components in countless products, rippled through the supply chain, leading to higher prices for Canadian consumers. The "consumer prices" for numerous goods experienced a noticeable surge.
- Steel: Increased tariffs on US steel directly translated to higher prices for Canadian manufacturers who relied on US steel imports, impacting the cost of automobiles, construction materials, and appliances.
- Aluminum: Similar increases were seen in aluminum products, affecting the price of everything from beverage cans to building materials. These price increases, in turn, affected "inflation" and the overall "cost of living."
- Lumber: The impact on the lumber industry, discussed in greater detail below, also contributed to higher construction and renovation costs.
Statistics Canada data showed a noticeable spike in the Consumer Price Index (CPI) following the implementation of tariffs, corroborating the impact on consumer prices.
H3: Reduced Purchasing Power
The increased cost of goods directly translated to reduced purchasing power for Canadian households. This "tariff impact" had a disproportionate effect on lower-income families, who faced increased financial strain. The impact on "disposable income" forced many to cut back on non-essential spending.
- Reduced Spending on Non-Essentials: Many Canadians reported cutting back on discretionary spending, such as dining out, entertainment, and travel. This decrease in consumer spending further dampened economic growth.
- Increased Financial Strain: The "economic hardship" caused by higher prices forced many households to re-evaluate their budgets and prioritize essential expenses, impacting their overall quality of life.
H2: Sector-Specific Analysis of Tariff Impacts
The effects of Trump's tariffs weren't uniform across all sectors. Some industries felt the impact more severely than others.
H3: The Automotive Industry
The Canadian automotive industry, deeply intertwined with the US economy, faced significant challenges due to "supply chain disruptions" caused by tariffs. The interconnected nature of "Canada-US trade" magnified the impact.
- Increased Input Costs: Higher prices for steel and aluminum, critical components in vehicle manufacturing, raised production costs and reduced competitiveness.
- Job Losses: Some automotive plants experienced reduced production or even temporary closures, leading to job losses and economic uncertainty.
H3: The Lumber Industry
The Canadian lumber industry faced retaliatory tariffs from the US, impacting "lumber exports" and leading to significant financial difficulties for Canadian producers. The ensuing "trade disputes" further complicated the industry’s challenges.
- Export Restrictions: The imposition of tariffs restricted access to the US market, a major export destination for Canadian lumber.
- Reduced Revenue: Reduced export volumes directly affected revenue for Canadian lumber producers, leading to layoffs and plant closures.
H3: Agriculture
Canadian agricultural exports to the US faced significant headwinds, with tariffs on certain products directly impacting "farmers" and increasing "food prices." This demonstrates the broad reach of “trade wars.”
- Reduced Market Access: Tariffs imposed by the US government reduced the competitiveness of Canadian agricultural products in the US market.
- Price Volatility: The uncertainty created by the tariffs led to price volatility and reduced predictability for Canadian farmers.
H2: Long-Term Consequences for Canadian Households
The effects of Trump's tariffs extended beyond the immediate impact on consumer prices and specific sectors.
H3: Economic Uncertainty and Investment
The uncertainty created by the trade disputes led to a decline in "consumer confidence" and reduced "investment." This "economic uncertainty" hindered long-term "economic growth."
- Delayed Investment Decisions: Businesses delayed investment plans due to the unpredictable trade environment.
- Reduced Consumer Spending: Uncertainty about future prices dampened consumer spending, further impacting economic growth.
H3: Shifts in Trade Relationships
Facing challenges in the US market, Canada actively pursued "trade diversification" and strengthened relationships with other trading partners. This shift towards "international trade" beyond the US was a long-term consequence of Trump's protectionist policies.
- New Trade Agreements: Canada actively pursued new trade agreements and partnerships to reduce its reliance on the US market.
- Strengthened Global Partnerships: Canada sought to strengthen its trade relationships with countries outside of North America to create a more resilient and diversified trading network.
3. Conclusion:
Trump's tariffs had a significant and lasting impact on Canadian households, leading to increased consumer prices, reduced purchasing power, and sector-specific challenges. The immediate consequences included higher costs for everyday goods and reduced disposable income, particularly impacting lower-income families. Long-term effects included economic uncertainty, reduced investment, and a shift in Canada's trade relationships. Understanding the multifaceted effects of these policies is crucial for navigating future trade negotiations. Understand the lasting impact of Trump's tariffs on Canadian households; learn more today!

Featured Posts
-
 Vacances Scolaires 2025 Quand Tombent Les Conges En Wallonie Bruxelles
Apr 23, 2025
Vacances Scolaires 2025 Quand Tombent Les Conges En Wallonie Bruxelles
Apr 23, 2025 -
 Whats Open And Closed On Easter In Prince Edward Island
Apr 23, 2025
Whats Open And Closed On Easter In Prince Edward Island
Apr 23, 2025 -
 Copper Market Forecast Tongling Highlights Us Tariff Risks
Apr 23, 2025
Copper Market Forecast Tongling Highlights Us Tariff Risks
Apr 23, 2025 -
 Velikiy Post 2025 Chistiy Ponedelnik Traditsii I Pravila Posta
Apr 23, 2025
Velikiy Post 2025 Chistiy Ponedelnik Traditsii I Pravila Posta
Apr 23, 2025 -
 Brice Turangs Bunt A Walk Off Victory For The Brewers
Apr 23, 2025
Brice Turangs Bunt A Walk Off Victory For The Brewers
Apr 23, 2025
