Economists Predict Rate Cuts Following Weak Retail Sales Figures
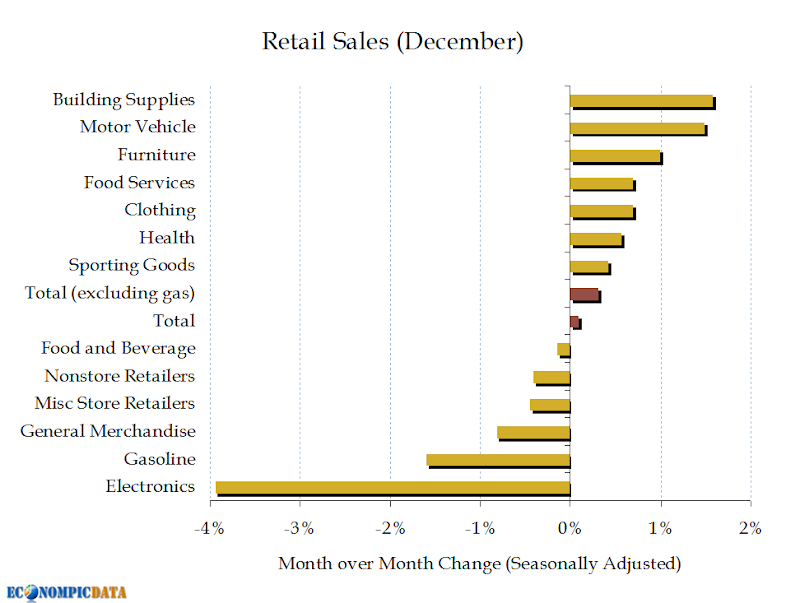
Table of Contents
Weak Retail Sales: The Driving Force Behind Rate Cut Predictions
The recent decline in retail sales figures is a major catalyst for the anticipated rate cuts. The percentage drop, while varying depending on the specific data source and region, paints a concerning picture of weakening consumer spending. This weakening is not isolated but reflects broader economic concerns.
-
The Retail Sales Decline: Reports from organizations such as the Bureau of Economic Analysis show a significant decrease in retail sales, indicating reduced consumer spending. This isn't merely a minor fluctuation; it represents a sustained trend that economists are closely monitoring.
-
Contributing Factors: Several factors are contributing to this decline in consumer spending. High inflation continues to erode purchasing power, leaving consumers with less disposable income. Rising interest rates, implemented to combat inflation, have increased borrowing costs, further dampening consumer confidence and impacting spending habits. Increased debt levels among households also limit their ability to spend.
-
Broader Economic Concerns: The weakness in retail sales isn't just a retail problem; it reflects a broader slowdown in economic activity. Decreased consumer spending directly impacts businesses, potentially leading to job losses and further reducing consumer confidence in a vicious cycle. This makes the overall economic outlook significantly more uncertain.
Central Bank Response: Why Rate Cuts Are Anticipated
Faced with weak retail sales and a potential economic slowdown, central banks are likely to respond by implementing rate cuts. This is a key component of monetary policy designed to stimulate economic activity.
-
The Role of Central Banks: Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve (Fed) in the United States and the European Central Bank (ECB), play a crucial role in managing inflation and fostering economic growth. Their primary tools are interest rate adjustments and other monetary policy measures.
-
Reasoning Behind Rate Cuts: By reducing interest rates, central banks aim to make borrowing cheaper. This incentivizes consumers to spend more and businesses to invest, thus boosting economic activity and hopefully countering the effects of weak retail sales. Lower interest rates also typically lower mortgage rates, making homeownership more accessible and potentially stimulating the housing market.
-
Specific Central Banks: While not all central banks will act simultaneously, many economists believe the Fed and ECB are likely to consider rate cuts in response to the economic data. The timing and magnitude of these cuts will depend on the evolving economic situation and inflation outlook.
-
Challenges of Rate Cuts: However, rate cuts are not without potential downsides. A premature reduction in interest rates could reignite inflationary pressures if demand suddenly increases too quickly. The effectiveness of rate cuts also depends on the underlying causes of the economic weakness. If the weakness is rooted in structural problems rather than simply a lack of consumer confidence, rate cuts may be less effective.
The Impact of Rate Cuts on Consumers and Businesses
Rate cuts will have a cascading impact on both consumers and businesses.
-
Lower Borrowing Costs: Lower interest rates translate to lower borrowing costs for individuals and businesses. This means lower interest payments on mortgages, auto loans, and other consumer loans. Businesses will also find it cheaper to borrow money for investment purposes.
-
Mortgage Rates and Consumer Loans: A direct consequence of rate cuts is a reduction in mortgage rates, making homeownership more affordable. Similarly, consumer loan repayments become less burdensome, freeing up disposable income for consumers.
-
Business Investment and Growth: Lower borrowing costs encourage businesses to invest in expansion, new equipment, and hiring. This boosts economic activity and job creation.
-
Effectiveness Concerns: While rate cuts can be a powerful stimulus, their effectiveness can be limited if consumers and businesses are hesitant to borrow or invest due to other economic uncertainties like persistently high inflation or fears of an impending recession.
Economic Outlook and Recession Risk
The weak retail sales figures and the anticipated rate cuts significantly impact the current economic outlook.
-
Current Economic Forecast: The economic forecast is currently uncertain. While rate cuts aim to stimulate growth, the ongoing effects of high inflation, geopolitical instability, and supply chain disruptions create considerable uncertainty.
-
Recession Probability: The probability of a recession is a key concern among economists. The weakening of consumer spending, coupled with other economic headwinds, increases the risk of a contraction in economic activity.
-
Expert Opinions: Many reputable economists are closely monitoring the situation and expressing concerns about the possibility of a recession. Their assessments vary, but the overall consensus is that the risk is elevated.
-
Rate Cuts and Recession Risk: Rate cuts are intended to mitigate recessionary risks by stimulating economic activity. However, if the underlying issues driving the economic slowdown are not addressed, rate cuts alone may not be sufficient to prevent a recession.
Conclusion
Weak retail sales figures have fueled predictions of imminent rate cuts by central banks. This move aims to stimulate economic growth and counteract the impact of reduced consumer spending. While rate cuts can offer some relief, their effectiveness depends on various economic factors, and the potential for a recession remains a significant concern. The interplay between inflation, consumer confidence, and central bank interventions will determine the future trajectory of the economy.
Call to Action: Stay informed about the evolving economic landscape and the implications of predicted rate cuts. Understanding how these shifts impact your finances is crucial. Continue to monitor news related to rate cuts, weak retail sales, and economic slowdown to make informed decisions about your financial planning.

Featured Posts
-
 The Impact Of Fatherhood On Bubba Wallaces Nascar Career
Apr 28, 2025
The Impact Of Fatherhood On Bubba Wallaces Nascar Career
Apr 28, 2025 -
 The Luigi Mangione Movement Perspectives From His Supporters
Apr 28, 2025
The Luigi Mangione Movement Perspectives From His Supporters
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Abwzby Kazakhstan Rhlat Jwyt Mbashrt Jdydt Me Tyran Alerbyt
Apr 28, 2025
Abwzby Kazakhstan Rhlat Jwyt Mbashrt Jdydt Me Tyran Alerbyt
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Building Voice Assistants Made Easy Open Ais 2024 Announcement
Apr 28, 2025
Building Voice Assistants Made Easy Open Ais 2024 Announcement
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Devin Williams Implosion Dooms Yankees Against Blue Jays
Apr 28, 2025
Devin Williams Implosion Dooms Yankees Against Blue Jays
Apr 28, 2025
