Analyzing Market Swings: Professional Vs. Individual Investor Behavior
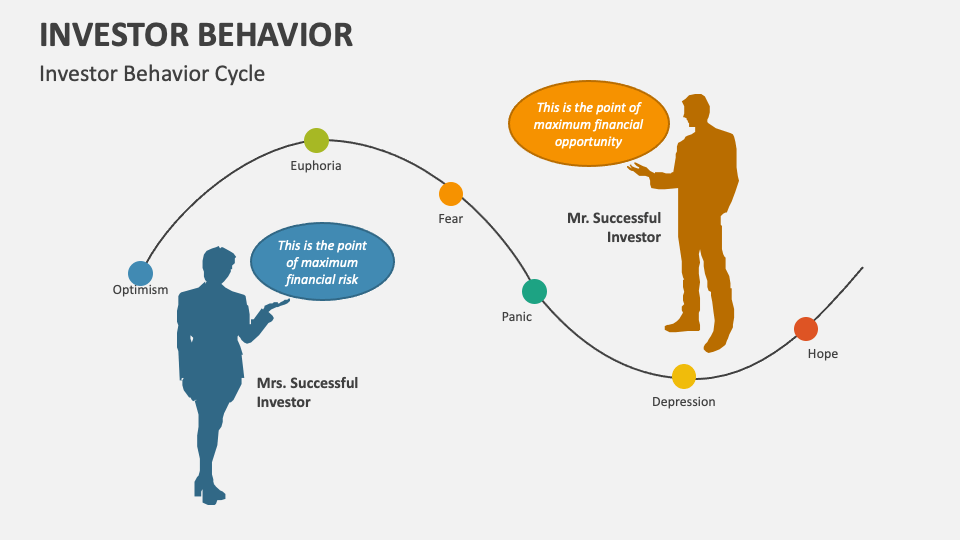
Table of Contents
Professional Investor Behavior During Market Swings
Professional investors, including fund managers, hedge fund managers, and institutional traders, approach market swings with a significantly different mindset than individual investors. Their actions are driven by rigorous analysis, sophisticated tools, and a long-term perspective.
Risk Management Strategies
Professionals prioritize risk management above all else. They employ a range of sophisticated techniques to mitigate potential losses and protect their capital. This includes:
- Diversification: They spread investments across various asset classes (stocks, bonds, real estate, commodities, etc.) to reduce the impact of any single market downturn. This diversification strategy is a cornerstone of professional portfolio management.
- Hedging: Utilizing derivatives like options and futures contracts to offset potential losses in other investments. This helps protect against adverse market movements.
- Stop-Loss Orders: These automatically sell an asset when it reaches a predetermined price, limiting potential losses. This is a crucial tool in active portfolio management.
- Stress Testing: Professionals regularly stress test their portfolios against various market scenarios (e.g., recessions, geopolitical events) to identify potential vulnerabilities and adjust their strategies accordingly. This proactive approach is key to long-term success.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Professional investors rely heavily on data and analytics to inform their decisions. Their approach is far more systematic and quantitative than that of individual investors. They utilize:
- Fundamental Analysis: In-depth research into a company's financial statements, management team, and industry to assess its intrinsic value.
- Technical Analysis: Studying historical price and volume data to identify patterns and predict future price movements.
- Algorithmic Trading: Employing sophisticated software and algorithms to execute trades automatically based on pre-defined parameters.
- Quantitative Models: Using complex mathematical models to forecast market trends and assess risk. These models often incorporate a vast array of economic indicators.
Long-Term Perspective
Unlike many individual investors, professionals typically adopt a long-term investment horizon. Their focus is on sustainable growth and value creation, rather than short-term gains. This means:
- Riding Out Volatility: They understand that short-term market fluctuations are normal and are prepared to weather these storms. They are less likely to panic-sell during market downturns.
- Strategic Asset Allocation: They carefully allocate assets across different classes based on long-term goals and risk tolerance. This involves a thorough understanding of market cycles.
- Value Investing: Identifying undervalued assets with the potential for significant long-term appreciation. This long-term outlook is crucial for maximizing returns.
Individual Investor Behavior During Market Swings
Individual investors, on the other hand, often approach market swings with less discipline and a greater susceptibility to emotional biases. Their actions are often influenced by fear, greed, and herd mentality.
Emotional Decision Making
Emotional biases significantly impact individual investor behavior during market swings. Common pitfalls include:
- Fear-Driven Selling: Panicking and selling assets during market downturns, often locking in losses at the worst possible time. This is a classic example of emotional decision-making.
- Greed-Driven Buying: Overconfidence and excessive risk-taking during bull markets, leading to inflated asset purchases. This often leads to substantial losses during subsequent market corrections.
- Herd Behavior: Following market trends blindly without conducting independent research or analysis. This can lead to buying high and selling low.
- Media Influence: Being swayed by media hype and misinformation, leading to impulsive investment decisions.
Limited Resources and Expertise
Individual investors often lack the resources and expertise of their professional counterparts. This includes:
- Access to Data: Limited access to sophisticated analytical tools, real-time market data, and research reports.
- Investment Knowledge: A less thorough understanding of complex financial instruments, market dynamics, and risk management strategies.
- Financial Advice: Many individual investors lack access to professional financial advisors who can provide guidance and support.
- Portfolio Diversification: Individual investors may have less diversified portfolios, making them more vulnerable to market fluctuations.
Short-Term Focus
Many individual investors focus on short-term gains, leading to:
- Frequent Trading: Trading frequently based on short-term market movements, incurring higher transaction costs and potentially losing out on long-term gains.
- Difficulty Weathering Corrections: Struggling to withstand market corrections, potentially selling assets at a loss. This short-term approach undermines long-term wealth building.
- Missed Opportunities: Failing to capitalize on long-term growth opportunities due to an emphasis on short-term results.
Key Differences in Response to Market Swings
The contrasting behaviors of professional and individual investors during market swings highlight key differences:
Risk Tolerance and Appetite
Professionals generally possess a higher risk tolerance and a more measured response to market fluctuations. They are better equipped to handle market volatility and are less likely to make impulsive decisions based on emotions.
Investment Strategies
Professionals rely on well-defined strategies backed by rigorous analysis and data. Individual investors may rely more on gut feelings, tips from friends, or market sentiment, increasing the risk of making poor investment choices.
Information and Resources
Professionals have far greater access to information, research, and analytical tools, enabling significantly more informed decision-making compared to individual investors.
Conclusion
Analyzing market swings reveals significant differences in the behavior of professional and individual investors. Professionals utilize sophisticated risk management, data-driven decision-making, and a long-term perspective. Individual investors, however, are more prone to emotional responses and short-term focus. Understanding these differences is crucial for all investors. By learning from the professional approach and mitigating emotional biases, individual investors can significantly improve their ability to navigate market swings and achieve their financial goals. To further enhance your understanding of analyzing market swings, consider seeking professional financial advice tailored to your individual circumstances and risk profile.

Featured Posts
-
 23 Xi Racing Announces New Sponsor For Bubba Wallace
Apr 28, 2025
23 Xi Racing Announces New Sponsor For Bubba Wallace
Apr 28, 2025 -
 New York Yankees Star Aaron Judge Welcomes Baby With Wife Samantha
Apr 28, 2025
New York Yankees Star Aaron Judge Welcomes Baby With Wife Samantha
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Current Gpu Prices A Look At The Market And Future Projections
Apr 28, 2025
Current Gpu Prices A Look At The Market And Future Projections
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Judge On 2026 Wbc A Look At The Potential Participation
Apr 28, 2025
Judge On 2026 Wbc A Look At The Potential Participation
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Yankees Offensive Outburst Highlights Max Frieds Winning Debut Against Pirates
Apr 28, 2025
Yankees Offensive Outburst Highlights Max Frieds Winning Debut Against Pirates
Apr 28, 2025
